Electron statistics detector
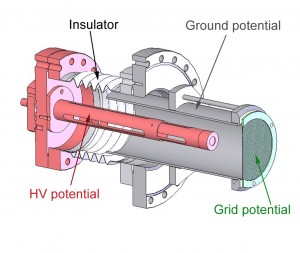
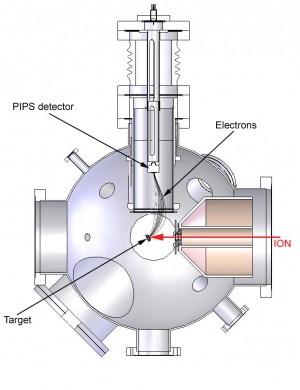 The electrons emitted from the target, due to an ion impact, are collected by the electric field produced by the grid potential (50-500 V). The grid is highly transparent and the electrons pass the grid and enter the interior region of the tube. The grounded tube and the Detector on HV potential (25-30 kV) act as a focusing electrostatic lens. When n electrons pass the grid, they all come from the same potential and are accelerated and focused onto the detector. Electron emission induced by a single projectile will be finished within less than 10-11 s, which is much shorter than the time resolution of the applied detector electronics (~10-6 s). Thus n electrons emitted due to a particular ion impact will be registered as one electron of n × 25 keV rather than n individual 25 keV electrons.
The electrons emitted from the target, due to an ion impact, are collected by the electric field produced by the grid potential (50-500 V). The grid is highly transparent and the electrons pass the grid and enter the interior region of the tube. The grounded tube and the Detector on HV potential (25-30 kV) act as a focusing electrostatic lens. When n electrons pass the grid, they all come from the same potential and are accelerated and focused onto the detector. Electron emission induced by a single projectile will be finished within less than 10-11 s, which is much shorter than the time resolution of the applied detector electronics (~10-6 s). Thus n electrons emitted due to a particular ion impact will be registered as one electron of n × 25 keV rather than n individual 25 keV electrons.
The energy sensitive detector gives a pulse corresponding to the number of electrons, which is then registered by the multi-channel-analyzer (MCA). The number of emitted electrons per HCI impact event is then obtained from the MCA spectrum by pulse height analysis.
Hollow atom formation and potential electron emission
Review:
F. Aumayr, and HP. Winter
Potential electron emission from metal and insulator surfaces
Springer Tracts in Modern Physics 225 (2007) 79 - 112 (takes a long time loading!)
J. Stöckl, T. Suta, F. Ditroi, HP. Winter, and F. Aumayr
Separation of potential and kinetic electron emission for grazing impact of multiply charged Ar ions on a LiF(001) surface
Physical Review Letters 93 (2004) 263201
C. Lemell, J. Stöckl, J. Burgdörfer, G. Betz, HP. Winter and F. Aumayr
Multicharged ion impact on clean Au(111): Suppression of kinetic electron emission in glancing angle scattering
Physical Review Letters 81 (1998) 1965 - 1968
J. Limburg, S. Schippers; R. Hoekstra, R. Morgenstern, H. Kurz, F. Aumayr and HP. Winter
Do hollow atoms exist in front of an insulating LiF surface
Physical Review Letters 75 (1995) 217 - 219
F. Aumayr, H. Kurz, D. Schneider, M.A. Briere, J.W. McDonald, C.E. Cunningham and HP. Winter
Emission of electrons from a clean gold surface induced by slow, very highly charged ions at the image charge acceleration limit
Physical Review Letters 71 (1993) 1943 - 1946
H. Kurz, K. Töglhofer, HP. Winter, F. Aumayr and R. Mann
Electron emission from slow hollow atoms at a clean metal surface
Physical Review Letters 69 (1992) 1140 - 1143
Energy loss
R.A. Wilhelm, E, Gruber, R. Ritter, R. Heller, S. Facsko, and F. Aumayr
Charge exchange and energy loss of slow highly charged ions in 1 nm thick carbon nanomembranes
Physical Review Letters 112 (2014) 153201 (5 pages)
PDF
J.I. Juaristi, C. Auth, H. Winter, A. Arnau, K. Eder, D. Semrad, F. Aumayr, P. Bauer, and P.M. Echenique
Unexpected Behaviour of the Stopping of Slow Ions in Ionic Crystals
Physical Review Letters 84 (2000) 2124 - 2127
C. Lemell, J. Stöckl, J. Burgdörfer, G. Betz, HP. Winter and F. Aumayr
Multicharged ion impact on clean Au(111): Suppression of kinetic electron emission in glancing angle scattering
Physical Review Letters 81 (1998) 1965 - 1968
K. Eder, D. Semrad, P. Bauer, R. Golser, P. Maier-Komor, F. Aumayr, M. Penalba, A. Arnau, J.M. Ugalde and P.M. Echenique
Absence of a “threshold effect” in the energy loss of slow protons traversing solid large band gap insulators
Physical Review Letters 79 (1997) 4112 - 4115
R. Golser, D. Semrad and F. Aumayr
Electronic stopping in a He-H2 mixture substantially exceeds Bragg's rule value
Physical Review Letters 76 (1996) 3104 - 3107
Contact: Walter Meissl, Daniel Winklehner