Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Jet
Usually plasma sources operated at atmospheric pressure are based
on arc discharges and produce thermal plasmas with temperatures
well above a few thousand K. We generated an Atmospheric Pressure
Plasma Jet in a capacitive radio-frequency (RF) plasma source, that
results in a stable glow-like discharge with a rather low gas
kinetic energy.
This kind of atmospheric pressure plasma sources provides a large
area of appliances in surfaces technology, like etching, coating,
disinfection, sterilisation and decontamination. Primary we focus
our work on the research of stability conditions and discharge
modes of the atmospheric plasma for various gas mixtures and
different geometrical and electrical performances.
The discharge used for the studies is generated between two planar
electrodes. One RF-powered, and the other grounded. Both electrodes
are water cooled to input an electrical power up to 500W and the
discharge is operated at a frequency of 13.56 MHz using an
impedance matching network. In our setup the powered RF electrode
is surrounded by grounded electrodes and separated from them by
insulators. This construction allows a variation of the gap spacing
between 0.5 and 2.5mm. Gas is injected through both side walls
close to the back side where the gap between RF and grounded
electrode is much larger. After flowing through the narrow gap
spacing, where the discharge is maintained, gas is exhausted into
ambient air.
The powered RF electrode is surrounded by grounded electrodes and separated from them by insulators.
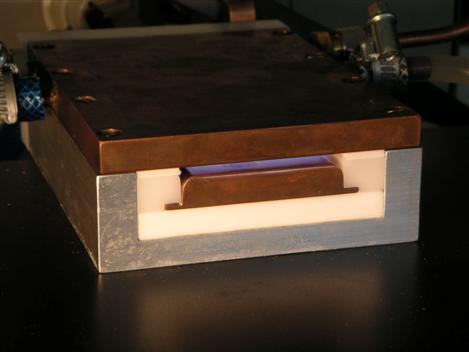
Up to now we run the plasma jet with Argon and Helium and various insulator materials. Other gases and mixtures will be tested in near future. The discharge gap was observed with optical instruments to investigate the discharge pattern between the electrodes. The voltage across the discharge and the current are measured simultaneously as well. Our new test setup will allow us to investigate the discharge pattern between the electrodes with optical spectrometer and cameras much more precisely.
